 Clove oil
Clove oil
Common name
Clove oil,Eugenol
ID
HD0018
Scientific name of the plant
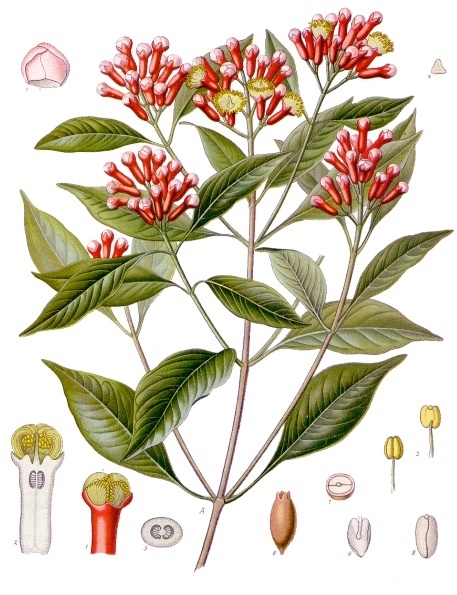
Syzygium aromaticum, synonyms Caryophyllus aromaticus, Eugenia aromatica, Eugenia caryophyllata, Eugenia caryophyllus
Anatomical part for use
flower, leaf, stem
Human use
Mouth and throat disorders
Summary
Cloves are the aromatic flower buds of a tree in the family Myrtaceae, Syzygium aromaticum. They are native to the Maluku Islands (or Moluccas) in Indonesia, and are commonly used as a spice. Cloves are available throughout the year owing to different harvest seasons in different countries. (Source: Wiki)
Evidence Level
Level 4 (Individual reports repeated observed over 5 years among different countries)
Hepatotoxicity reports in literature
Hepatotoxicity Description
The low concentrations of eugenol and clove extracts used topically and in herbal products have not been convincingly linked to instances of liver injury, either in the form of serum enzyme elevations or clinically apparent liver injury. In high doses, however, eugenol appears to be a direct cytotoxin and several instances of severe acute liver and kidney injury have been reported after accidental overdose of eugenol containing herbal products, largely in children. Overdoses have been marked by the onset of agitation, decrease in consciousness and coma arising within hours on ingestion (10-30 mL of clove oil). There is typically an accompanying acidosis, respiratory depression and severe hypoglycemia requiring ventilation and intravenous glucose. Liver injury arises 12 to 24 hours after ingestion with marked elevations in serum aminotransferase levels and early coagulation abnormalities. Signs of hepatic failure arise rapidly, and jaundice can develop and deepen. The overall clinical presentation is typical of acute hepatic necrosis and similar to that of acetaminophen, iron or copper overdose. The liver injury generally worsens for several days but then rapidly improves and ultimately resolves within 1 to 3 weeks. Renal dysfunction may also occur but rarely requires intervention or dialysis. Long term injury or effects have not been described. Cases described in the literature have been in infants who swallowed clove oil being used by parents. (Source: LiverTox)
Potential medicinal uses and adverse effects
Long-used in traditional medicine, there is evidence that clove oil containing eugenol is effective for toothache pain and other types of pain, and one review reported efficacy of eugenol combined with zinc oxide as an analgesic for alveolar osteitis. Studies to determine its effectiveness for fever reduction, as a mosquito repellent, and to prevent premature ejaculation have been inconclusive. It remains unproven whether blood sugar levels are reduced by cloves or clove oil. Use of clove for any medicinal purpose has not been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration, and its use may cause adverse effects if taken orally by people with liver disease, blood clotting and immune system disorders, or food allergies. (Source: Wiki)
Traditional medicinal uses
Cloves are used in traditional medicine as the essential oil, which is used as an anodyne (analgesic) mainly for dental emergencies and other disorders. The essential oil is used in aromatherapy. (Source: Wiki)

Common name
Clove oil,Eugenol
ID
HD0018
Scientific name of the plant
Syzygium aromaticum, synonyms Caryophyllus aromaticus, Eugenia aromatica, Eugenia caryophyllata, Eugenia caryophyllus
Anatomical part for use
flower, leaf, stem
Human use
Mouth and throat disorders
Summary
Cloves are the aromatic flower buds of a tree in the family Myrtaceae, Syzygium aromaticum. They are native to the Maluku Islands (or Moluccas) in Indonesia, and are commonly used as a spice. Cloves are available throughout the year owing to different harvest seasons in different countries. (Source: Wiki)
Evidence Level
Level 4 (Individual reports repeated observed over 5 years among different countries)
Hepatotoxicity reports in literature
Hepatotoxicity Description
The low concentrations of eugenol and clove extracts used topically and in herbal products have not been convincingly linked to instances of liver injury, either in the form of serum enzyme elevations or clinically apparent liver injury. In high doses, however, eugenol appears to be a direct cytotoxin and several instances of severe acute liver and kidney injury have been reported after accidental overdose of eugenol containing herbal products, largely in children. Overdoses have been marked by the onset of agitation, decrease in consciousness and coma arising within hours on ingestion (10-30 mL of clove oil). There is typically an accompanying acidosis, respiratory depression and severe hypoglycemia requiring ventilation and intravenous glucose. Liver injury arises 12 to 24 hours after ingestion with marked elevations in serum aminotransferase levels and early coagulation abnormalities. Signs of hepatic failure arise rapidly, and jaundice can develop and deepen. The overall clinical presentation is typical of acute hepatic necrosis and similar to that of acetaminophen, iron or copper overdose. The liver injury generally worsens for several days but then rapidly improves and ultimately resolves within 1 to 3 weeks. Renal dysfunction may also occur but rarely requires intervention or dialysis. Long term injury or effects have not been described. Cases described in the literature have been in infants who swallowed clove oil being used by parents. (Source: LiverTox)
Potential medicinal uses and adverse effects
Long-used in traditional medicine, there is evidence that clove oil containing eugenol is effective for toothache pain and other types of pain, and one review reported efficacy of eugenol combined with zinc oxide as an analgesic for alveolar osteitis. Studies to determine its effectiveness for fever reduction, as a mosquito repellent, and to prevent premature ejaculation have been inconclusive. It remains unproven whether blood sugar levels are reduced by cloves or clove oil. Use of clove for any medicinal purpose has not been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration, and its use may cause adverse effects if taken orally by people with liver disease, blood clotting and immune system disorders, or food allergies. (Source: Wiki)
Traditional medicinal uses
Cloves are used in traditional medicine as the essential oil, which is used as an anodyne (analgesic) mainly for dental emergencies and other disorders. The essential oil is used in aromatherapy. (Source: Wiki)